
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the way companies conduct user research and software testing. From automating surveys and interview analysis to detecting and fixing vulnerabilities and bugs before software is released, AI has made research and testing more efficient, scalable, and insightful. However, as with any technological advancement, AI comes with limitations, challenges, and ethical concerns that organizations must consider.
Here’s what you’ll learn in this article:
- How AI is Used in User Research & Software Testing in 2025
- How Effective is AI in User Research & Software Testing?
- An AI Bot Will Never be a Human: Challenges & Limitations of AI
- Beware of Fraud and Ethical Issues of Using AI in User Research & Marketing
- The Best Way to Use AI in User Research & Software Testing
- The Future of AI in User Research & Software Testing
AI is already making a significant impact in user research and software testing, helping teams analyze data faster, uncover deeper insights, and streamline testing processes. Here are some of the most common applications:
How AI is Used in User Research in 2025
User research often involves analyzing large volumes of qualitative feedback from interviews, surveys, and product usage data: a process that AI is helping to streamline. AI-powered tools can automate transcription, sentiment analysis, survey interpretation, and even simulate user behavior, allowing researchers to process insights more efficiently while focusing on strategic decision-making.
Survey Feedback Analysis & Summarization
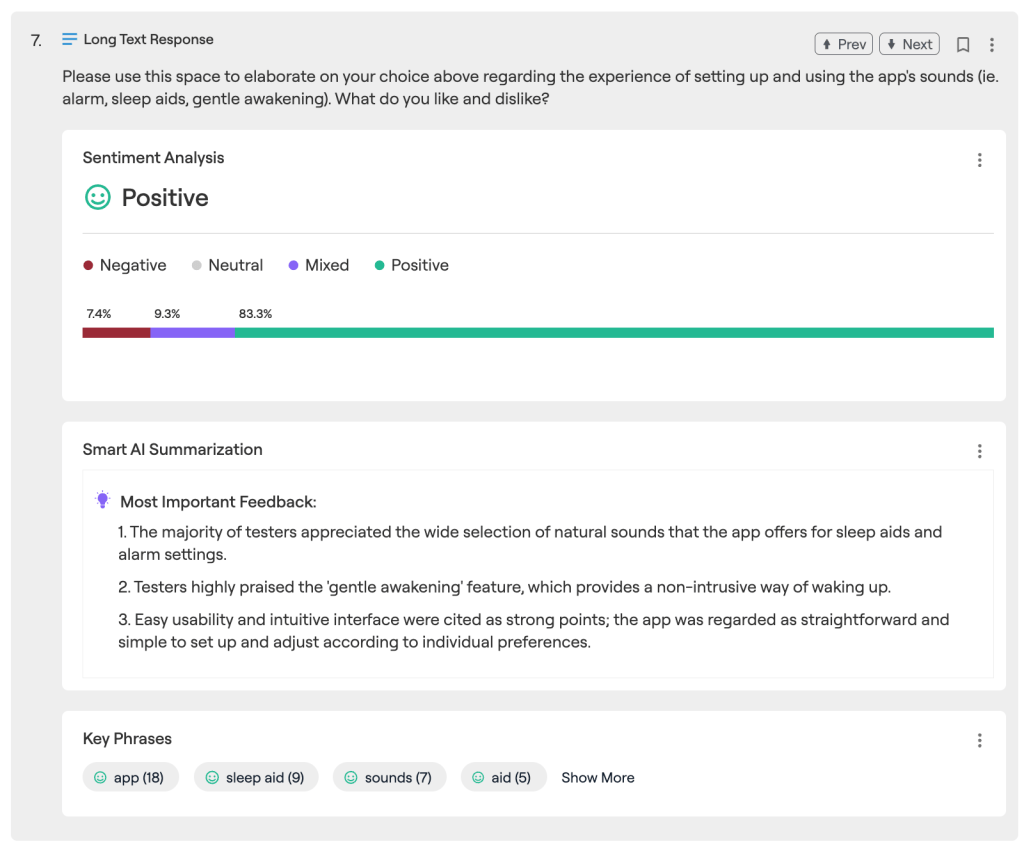
AI tools can help categorize, summarize, and annotate survey responses, allowing researchers to extract instant insights instead of manually reviewing thousands of answers. While very effective, AI-generated insights still require human review to ensure accuracy and capture nuance.
Examples: Most survey platforms include AI analysis features, including Qualtrics, SurveyMonkey, and our own survey tool on BetaTesting.
Automated Transcription (in Videos or Audio)
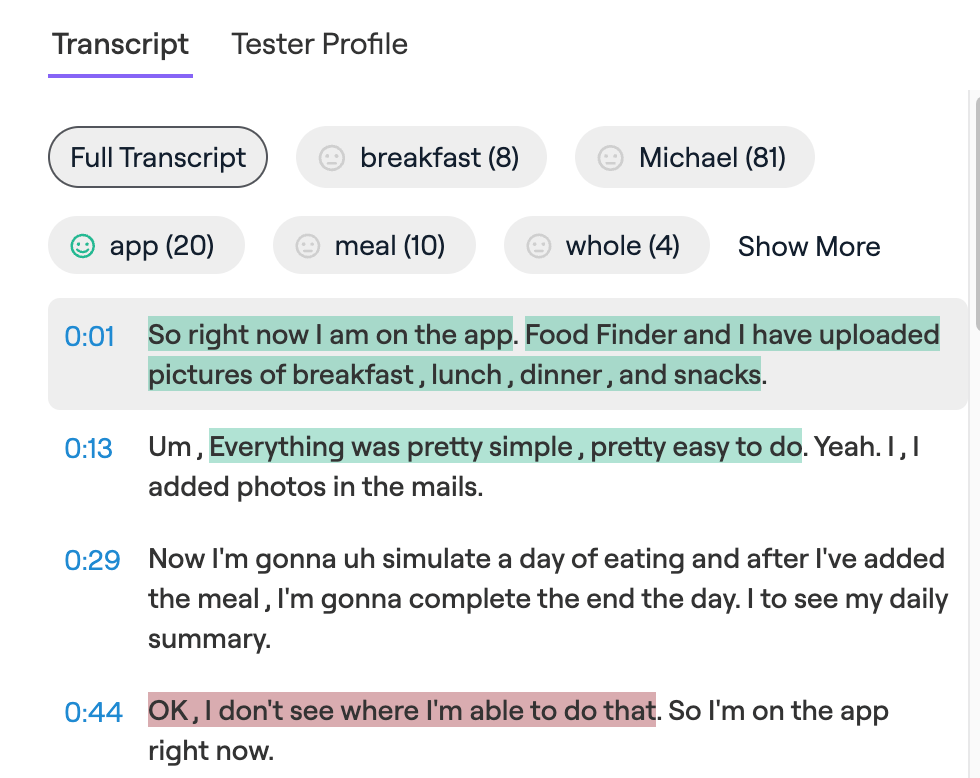
Transcription is the process of converting audio into written words.
It wasn’t that long ago that user researchers had to manually transcribe video recordings associated with user interviews and usability videos. Now, videos and audio are automatically transcribed by many tools and research platforms, saving countless hours and even providing automatic language translation, feedback, and sentiment analysis. This allows researchers to more easily identify key themes and trends across large datasets.
Check it out: Audio transcription tools include products like Otter.ai, Sonix.ai, and ChatGPT’s Speech to Text, and countless developer APIs like ChatGPTs Audio API, Amazon Transcribe, and Google Cloud’s Speech-to-Text and Video Intelligence APIs.
Automated Video Analysis

Transcribing video is just the tip of the iceberg. After getting a transcription, AI tools can then analyze the feedback for sentiment, categorize and annotate videos, and provide features that make it easier for humans to stream and analyze videos directly. In addition, audio analysis and video analysis tools can detect tone, emotion, facial expressions, and more.
Check it out: Great examples include Loom’s AI video analysis functionality, and our own AI video analysis tool on BetaTesting.
Feedback Aggregation into Research Repositories
Using some of the functionality outlined above, AI can help analyze, tag, categorize, and summarize vast amounts of data. AI can help take both unstructured (e.g. videos or call transcripts) and structured data (e.g. surveys, forms) in a wide variety of formats, and make the data structured and searchable in a standard way. In doing so, the data can be further analyzed by statistical software and other business intelligence tools. You can learn more about Research Repositories here.
This will become extremely useful for large enterprises that are constantly generating customer feedback. Feedback that was once lost or never captured at all can now be piped into the feedback repository and used to inform everything from product development to customer support and business strategy.
Check it out: Some examples for research repositories include Marvin, Savio, ProductBoard
AI-Powered User Interviewers
Some startups are testing AI virtual interviewers like Wondering and Outset.ai. ChatGPT-based chatbots can also be used to conduct and analyze user interviews.
This is very interesting, and there is certainly a valid use case for conducting AI-led interviews and surveys. After all, there’s no need for scheduling and it can certainly help reduce costs and make it much easier to conduct interviews at scale. It can also reduce interviewer bias and standardize questioning. However, obviously AI bots are not humans. They lack real emotion and are not very good at complex reasoning. This is not something that will replace real user interviews.
Let’s not forget that the user is the most important part of a user interview. Is a user interested in being interviewed for 30-60 minutes by an AI bot? If so, it’s a much more limited experience. Also, a key component of the costs for user interviews are the incentives for participants. This doesn’t change, whether it’s an AI or a real human conducting the interview. If you want good data from the right audience, it requires meaningful incentives.
Synthetic AI Participants

Some startups like Synthetic Users are exploring AI-generated user personas that simulate real users for the purpose of surveys or user interviews. While useful for modeling interactions and opinions at scale, synthetic users cannot replicate real-world unpredictability, emotions, or decision-making.
Human feedback remains essential. Synthetic users are only as good as the data that powers them. Right now AI bots are essentially empty, soulless veneers that write, sound, and and may soon appear to be human, but their reasoning, decision making, and opinions are only a hollow representation of how a real human may sound or write in a similar situation. Until AI decision making is driven by the same depth of data that powers our own decision making as humans, “synthetic users” are an interesting idea, but they are not research participants. They are more akin to reading market research analysis reports about how a specific population segment feels about X.
As AI evolves, its ability to automate and analyze research data will improve, but the human element remains essential for capturing deeper insights and ensuring meaningful results. The best approach blends AI-driven efficiency with human expertise for more accurate and insightful user research.
AI in Software Development and Testing

AI has significantly transformed software development and quality assurance, making code more efficient, accurate, scalable, and bug free. By automating repetitive tasks, detecting bugs earlier, and optimizing test scripts, AI reduces manual effort and improves the overall reliability of software. AI-powered testing not only speeds up development cycles but also enhances test coverage, security, and performance monitoring, allowing teams to focus on more strategic aspects of software quality.
Auto-Repairing Automated QA Test Scripts
Automated testing tools like Rainforest, Testim and Functionize can generate and adjust test scripts automatically, even when UI elements change. This eliminates the need for manual script maintenance, which is traditionally time-consuming and prone to human error. By leveraging AI, testing teams can increase test stability, adapt to UI updates seamlessly, and reduce the burden of rewriting scripts whenever the software evolves.
Code Analysis for Bugs and Vulnerabilities
Tools like Snyk, Codacy, and GitHub Dependabot scan codebases in real time to detect potential bugs, security vulnerabilities, and inefficiencies. By identifying issues early in the development cycle, AI helps developers prevent costly fixes later in development. These tools also provide automated recommendations for refactoring, improving both code quality and maintainability over time.
Code Improvement & Refactoring
AI tools can help write code from scratch, re-write, reformat, and improve code quality. Common tools and models currently include ChatGPT / OpenAI o1, Anthropic Sonnet 3.7, Github Copilot and Codebuddy. Some tools include IDE integration like JetBrains AI Assistant.
While AI will not replace developers, it will definitely change the way developers work, and already is. Spreadsheets and software did not replace statisticians and accountants, but they certainly changed everything about these jobs.
Other AI-Powered Software Testing Uses
Beyond script generation and code analysis, AI is revolutionizing software testing in several other ways. AI-powered visual regression testing ensures that unintended UI changes do not affect user experience by comparing screenshots and detecting anomalies. Predictive AI models can forecast test failures by analyzing historical test data, helping teams prioritize high-risk areas and focus on the most critical test cases. Additionally, AI chatbots can simulate real user interactions to stress-test applications, ensuring that software performs well under different scenarios and usage conditions.
Synthetic users also have a role to plan in automated load testing. Already, automated load testing tools help script and simulate end-user actions to test an app’s infrastructure (APIs, backend, database, etc) to ensure it can handle peak loads. In the future, automated synthetic users can behave more naturally and unpredictably, simulating a real user’s usage patterns.
As AI technology continues to evolve, automated testing will become more sophisticated, further reducing manual workload, improving accuracy, and enhancing overall software reliability. However, human oversight will remain essential to validate AI-generated results, handle complex edge cases, and conduct real world testing in real world environments.
How Effective is AI in User Research & Software Testing?

What AI Does Better Than Humans
AI offers some clear advantages over traditional human-led research and testing, particularly in areas that require speed, pattern recognition, and automation. While human intuition and creativity remain invaluable, AI excels in handling large-scale data analysis, repetitive tasks, and complex pattern detection that might take humans significantly more time and effort to process.
- Cost Savings
- AI can dramatically reduce the hours required for manual data analysis and testing, allowing companies to cut costs on large research and development teams.
- Traditional testing and analysis require a significant investment in personnel, training, and tools, whereas AI-powered solutions streamline workflows with minimal human intervention.
- Additionally, AI-driven automation reduces errors caused by human fatigue, further increasing efficiency and accuracy.
- Time & Resource Efficiency
- One of AI’s greatest strengths is its ability to process vast amounts of data in a fraction of the time it would take a human team. For example: AI models can generate real-time insights, allowing companies to respond faster to usability issues, performance bottlenecks, or security vulnerabilities.
- AI can analyze thousands of user responses from surveys, beta tests, or feedback forms within minutes, compared to the weeks it would take human researchers to sift through the same data manually.
- In software testing, AI-powered automation tools can run millions of test cases across different devices, operating systems, and conditions simultaneously, something human testers cannot do at scale.
- Identifying Hidden Patterns & Insights
- AI is uniquely capable of uncovering trends and anomalies that humans might overlook due to cognitive biases or data limitations. This capability is particularly useful in:
- User behavior analysis: AI can detect subtle shifts in customer preferences, pinpointing emerging trends before they become obvious to human researchers.
- Software performance monitoring: AI can recognize recurring crash patterns, latency spikes, or performance issues that would take human testers far longer to detect.
- Fraud and anomaly detection: AI can identify unusual user activities, such as cheating in product testing or fraudulent behavior, by spotting patterns that would otherwise go unnoticed.
By leveraging AI for these tasks, companies can achieve greater efficiency, gain deeper insights, and make faster, data-driven decisions, ultimately improving their products and customer experiences.
An AI Bot Will Never be a Human: Challenges & Limitations of AI

We might as well rub it in while we can: An AI bot will NEVER be a human.
AI offers efficiency and automation, but it isn’t foolproof. Its effectiveness depends on data quality, human oversight, and the ability to balance automation with critical thinking.
Can AI-Generated Data Be Trusted?
AI is only as good as the data it’s trained on. If the underlying data contains biases, gaps, or inaccuracies, AI-generated insights will reflect those same flaws. For example, AI models may reinforce historical biases, skewing research outcomes. They can also misinterpret behaviors from underrepresented groups due to data gaps, leading to misleading trends. Additionally, AI systems trained on incomplete or noisy data may produce unreliable results, making human validation essential for ensuring accuracy.
Can AI really be intelligent like a human?
Probably not for a long time. AI is running out of training data, or at the very least, it’s using AI generated content that it doesn’t even know is AI-generated content. As AI content becomes more omnipresent, and AI trains AI with AI data, there’s a real risk that the output from AI models becomes worse over time, or at least plateaus. We can continue to make it more useful, and built into meaningful applications in our daily life, but is it going to continue getting smarter exponentially?
Are we on the cusp of an AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) breakthrough, or did we just take a gigantic leap, and the rest will be normal-speed technological progress over time? More than likely it’s the latter. AI is not going to replace humans, but it’s going to be an amazing tool.
AI Lacks Context & Complex Reasoning
While AI excels at pattern recognition, it struggles with nuance, emotion, and deeper reasoning. It often misreads sarcasm, cultural subtleties, or tone in sentiment analysis, making it unreliable for qualitative research. AI also lacks contextual understanding, meaning it may draw inaccurate conclusions when presented with ambiguous or multi-layered information. Furthermore, because AI operates within the constraints of its training data, it cannot engage in critical thinking or adapt beyond predefined rules, making it unsuitable for tasks requiring deep interpretation and human intuition.
AI Still Needs Supervision
Despite its ability to automate tasks, AI requires human oversight to ensure accuracy and fairness. Without supervision, AI may misinterpret data trends, leading to incorrect insights that impact decision-making. Additionally, unintended biases can emerge, particularly in research areas such as hiring, financial assessments, or product testing. Companies that overly rely on AI recommendations without expert review risk making decisions based on incomplete or misleading data. AI should support human decision-making, not replace it, ensuring that findings are properly validated before being acted upon.
Synthetic Users Are Not Real Users
AI-generated testers and research participants provide a controlled environment for testing, but they cannot fully replicate human behaviors. AI obviously lacks the ability to have genuine emotion, spontaneous reactions, and the subtle decision-making processes that shape real user experiences. It also fails to account for real-world constraints, such as physical, cognitive, and environmental factors, which influence user interactions with products and services. Additionally, synthetic users tend to exhibit generalized behaviors, reducing the depth of insights that can be gathered from real human interactions. While AI can assist in preliminary testing, real user input remains irreplaceable for truly understanding customer needs.
AI Can Impact Human Behavior
The presence of AI in research and testing can unintentionally alter how people respond. Users often engage differently with AI-driven surveys or chatbots than they do with human researchers, which can introduce bias into the data. Furthermore, AI-driven research may lack trust and transparency, leading participants to modify their responses based on the perception that they are interacting with a machine rather than a person. Without human researchers to ask follow-up questions, probe deeper into responses, or interpret emotional cues, AI-driven studies may miss valuable qualitative insights that would otherwise be captured in human-led research.
The bottom line is that AI enhances efficiency, but it cannot replace human judgment, critical thinking, or authentic user interactions. Companies must balance automation with human oversight to ensure accurate, fair, and meaningful research outcomes. AI works best as a tool to enhance human expertise, not replace it, making collaboration between AI and human researchers essential for trustworthy results.
Beware of Fraud, Fake Users, and other Ethical Issues
AI also introduces major problems for the user research industry as a whole. In the future, it will be increasingly challenging to discern real behavior and feedback from fake AI-driven behavior and bots.
Read our article about Fraud and Ethics Concerns in AI User Research and Testing.
Some of the biggest concerns around the use of AI revolve around fake users, automated attacks, and identity spoofing. AI is making it easier than ever for fraudsters to create fake users, manipulate identities, and automate large-scale attacks on software platforms. From AI-generated synthetic identities and location spoofing to automated bot interactions and CAPTCHA-solving, fraud is becoming more sophisticated and harder to detect. Fake users can skew engagement metrics, manipulate feedback, and exploit region-specific programs, leading to distorted data and financial losses. Worse yet, AI-powered fraud can operate at scale, flooding platforms with fabricated interactions that undermine authenticity.
To stay ahead, platforms must fight AI with AI: leveraging fraud detection algorithms, behavioral analytics, and advanced identity verification to spot and eliminate fake users. At BetaTesting, we’re leading this fight with numerous fraud detection and anti-bot practices in place to ensure our platform can maintain the high quality that we expect. These measures include many of those referenced above, including IP detection and blocking, ID verification, SMS verification, duplicate account detection, browsing pattern detection, and more.
The Best Way to Use AI in User Research & Software Testing
AI is a powerful tool that enhances, rather than replaces, human researchers and testers. The most effective approach is a collaborative one: leveraging AI for data processing, automation, and pattern recognition while relying on human expertise for nuanced analysis, decision-making, and creativity.
AI excels at quickly identifying patterns and trends in user feedback, but human interpretation is essential to extract meaningful insights and contextual understanding. Likewise, in software testing, AI can automate repetitive tasks such as bug detection and performance monitoring, freeing human testers to focus on real-world usability, edge cases, and critical thinking.
Organizations that use AI as a complement to human expertise, rather than a substitute, will see the greatest benefits. AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data efficiently, when combined with human intuition and strategic thinking, results in faster, more accurate, and more insightful research and testing.
The Future of AI in User Research & Software Testing
AI’s role in research and testing will continue to evolve, becoming an indispensable tool for streamlining workflows, uncovering deeper insights, and handling large-scale data analysis. As AI-powered tools grow more sophisticated, research budgets will increasingly prioritize automation and predictive analytics, enabling teams to do more with fewer resources. However, human oversight will remain central to ensuring the accuracy, relevance, and ethical integrity of insights.
AI’s ability to detect patterns in user behavior will become more refined, identifying subtle trends that might go unnoticed by human analysts. It will assist in generating hypotheses, automating repetitive tasks, and even simulating user interactions through synthetic participants. However, real human testers will always be necessary to capture emotional responses, unpredictable behavior, and contextual nuances that AI alone cannot fully grasp.
While the role of AI will continue to expand, the future of research and testing belongs to those who strike the right balance between AI-driven efficiency and human expertise. Human researchers will remain the guiding force: interpreting results, asking the right questions, and ensuring that research stays grounded in real-world experiences. Companies that embrace AI as an enhancement rather than a replacement will achieve the most accurate, ethical, and actionable insights in an increasingly data-driven world.
Fraud & Ethics!!! AI is transforming user research and software testing, but its growing role raises ethical concerns around job displacement, transparency, and the authenticity of insights. While AI can enhance efficiency, companies must balance automation with human expertise and ensure responsible adoption to maintain trust, fairness, and meaningful innovation. Read our article about Fraud and Ethics Concerns in AI User Research and Testing.
Final Thoughts
AI is reshaping user research and software testing, making processes faster, smarter, and more scalable. However, it can’t replace human intuition, creativity, and oversight. The best approach is to use AI as a powerful assistant: leveraging its speed and efficiency while ensuring that human expertise remains central to the research and testing process.
As AI evolves, businesses must navigate its opportunities and ethical challenges, ensuring that AI-driven research remains trustworthy, unbiased, and truly useful for building better products and user experiences.
Have questions? Book a call in our call calendar.
