-
Top 5 Mistakes Companies Make In Beta Testing (And How to Avoid Them)

Beta testing is a pivotal phase in the software development lifecycle, offering companies invaluable insights into their product’s performance, usability, and market fit. However, missteps during this phase can derail even the most promising products. Let’s delve into the top five mistakes companies often make during beta testing and how to avoid them, supported by real-world examples and expert opinions.
Here’s what you need to avoid:
- Don’t launch your test without doing basic sanity checks
- Don’t go into it without the desire to improve your product
- Don’t test with the wrong beta testers or give the wrong incentives
- Don’t recruit too few or too many beta testers
- Don’t seek only positive feedback and cheerleaders
1. Failing to do sanity tests for your most basic features.
Jumping straight into beta testing without validating that your latest build actually works is a recipe for disaster.
If your app requires taking pictures, but crashes every time someone clicks the button to snap a picture, why are you wasting your time and money on beta testing?!
Set up an internal testing program with your team:
Alpha testing can be done internally to help identify and rectify major bugs and issues before exposing the product to external users. This has been a lesson learned by many in the past, and it’s especially true if you are hoping to get user experience or usability feedback. If your app just doesn’t work, the rest of your feedback is basically meaningless!
Google emphasizes the importance of internal testing:
“Dogfooding is an important part of our test process. Test teams do their best to find problems before dogfooding, but we all know that testing by dedicated testers only goes so far.” – Inc.com
Next, you need to ensure every build goes through a sanity test prior to sending it out to testers
It doesn’t matter if your developers just tweaked one line of code. If something changed in the code, it’s possible it broke the entire app. Before sending out a product to external testers for the purpose of testing or user research, ensure your team has personally tested all the major product features for that exact build. It doesn’t matter if you’ve tested it 1,000 times before, it needs to be tested again from scratch.
How do you avoid this mistake?
Conduct thorough internal testing (alpha phase) to test your product internally before testing externally. Never test a build with testers that your team hasn’t personally tested and validated that the core features work.
2. Don’t go into it without the desire to improve your product

Your goal for testing should be research-related. You should be focused on collecting user feedback and/or data, and resolving issues that ultimately allow you to improve your product or validate that your product is ready for launch. You can have secondary goals, yes. For example, the desire to collect testimonials or reviews you can use for marketing reasons, or beginning to build your user base.
You should have a clear goal about what you plan to accomplish. Without a clear goal and plan for testing, beta testing can become chaotic and difficult to analyze. A lack of structure leads to fragmented or vague feedback that doesn’t help the product team make informed decisions.
How do you avoid this mistake?
Go into it with specific research-related goals. For example: to learn from users so you can improve your product, or to validate that your product is ready for launch. Ideally, you should be OK with either answer – e.g. “No, our product is not ready for launch. We need to either improve it or kill it before we waste millions on marketing.”
3. Don’t Test with the Wrong Beta Testers
Selecting testers who don’t reflect your target market can result in misleading feedback. For instance, many early-stage apps attract tech enthusiasts during open beta—but if your target audience is mainstream users, this can cause skewed insights. Mismatched testers often test differently and expect features your actual users won’t need.
Make sure you’re giving the right incentives that align with your target audience demographics and what you’re asking of testers. For example, if you’re recruiting a specialized professional audience, you need to offer meaningful rewards – you aren’t going to recruit people that make 150K to spend an hour testing for a $15 reward! Also, if your test process is complex, difficult, or just not fun – that matters. You’ll need to offer a higher incentive to get quality participation.
How do you avoid this mistake?
Recruit a tester pool that mirrors your intended user base. Tools like BetaTesting allow you to target and screen testers based on hundreds of criteria (demographic, devices, locations, interests, and many others) to ensure that feedback aligns with your customer segment. Ensure that you’re providing meaningful incentives.
4. Don’t Recruit Too Few or Too Many Beta Testers.

Having too few testers means limited insights and edge-case technical issues will be missed. Conversely, having too many testers is not a great use of resources. It costs more, and there are diminishing returns. At a certain point, you’ll see repetitive feedback that doesn’t add additional value.Too many testers can also overwhelm your team, making feedback difficult to analyze or prioritize insights.
How do you avoid this mistake?
For most tests, focus on iterative testing with groups of 5-100 testers at a time. Beta testing is about connecting with your users, learning, and continuously improving your product. When do you need more? If your goal is real-world load testing or data collection, those are cases where you may need more testers. But in that case, your team (e.g. engineers or data scientists) should be telling you exactly how many people they need and for what reason. It shouldn’t be because you read somewhere that it’s good to have 5,000 testers.
5. Don’t seek only positive feedback and cheerleaders
Negative feedback hurts. After pouring your heart and soul into building a product, negative feedback can feel like a personal attack. Positive feedback is encouraging, and gives us energy and hope that we’re on the right path! So, it’s easy to fall into the trap of seeking out positive feedback and discounting negative feedback.
In reality, it’s the negative feedback that is often most helpful. In general, people have a bias to mask their negative thoughts or hide them altogether. So when you get negative feedback. even when it’s delivered poorly, it’s critical to pay attention. This doesn’t mean that every piece of feedback is valid or that you need to build every feature that’s requested. But you should understand what you can improve, even if you choose not to prioritize it. You should understand why that specific person felt that way, even if you decide it’s not important.
The worst behavior pattern that we see: Seeking positive feedback and validation and discounting or excluding negative feedback. This is a mental/phycological weakness that will not lead to good things.
How do you avoid this mistake?
View negative feedback as an opportunity to learn and improve your product. Most people won’t tell you how they feel. Perhaps this is a good chance to improve something that you’ve always known was a weakness or a problem.
Conclusion
Avoiding these common pitfalls can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your beta testing phase, leading to a more refined product and successful launch. By conducting thorough alpha testing, planning meticulously, selecting appropriate testers, managing tester numbers wisely, and keeping testers engaged, companies can leverage beta testing to its fullest potential.
Have questions? Book a call in our call calendar.
-
Giving Incentives for Beta Testing & User Research

In the realm of user research and beta testing, offering appropriate incentives is not merely a courtesy but a strategic necessity. Incentives serve as a tangible acknowledgment of participants’ time and effort, significantly enhancing recruitment efficacy and the quality of feedback obtained.
This comprehensive blog article delves into the pivotal role of incentives, exploring their types, impact on data integrity, alignment with research objectives, and strategies to mitigate potential challenges such as participant bias and fraudulent responses.
Here’s what you’ll learn in this article:
- The Significance of Incentives in User Research
- Types of Incentives: Monetary and Non-Monetary
- Impact of Incentives on Data Quality
- Aligning Incentives with Research Objectives
- Matching Incentives to Participant Demographics
- Mitigating Fraud and Ensuring Data Integrity
- Best Practices for Implementing Incentives
- Incentives Aren’t Just a Perk—They’re a Signal
The Significance of Incentives in User Research
Incentives play a pivotal role in the success of user research studies, serving multiple critical functions:
1. Enhancing Participation Rates
Most importantly, incentives help researchers recruit participants and get quality results.
Offering incentives has been shown to significantly boost response rates in research studies. According to an article by Tremendous, “Incentives are proven to increase response rates for all modes of research.”
The article sites several research studies and links to other articles like “Do research incentives actually increase participation?” Providing the right Incentives makes it easier to recruit the right people, get high participation rates, and high-quality responses. Overall, they greatly enhance the reliability of the research findings.
2. Recruiting the Right Audience & Reducing Bias
By attracting the right participant pool, incentives mitigate selection bias and ensure your findings are accurate for your target audience.
For example, if you provide low incentives that only appeal to desperate people, you aren’t going to be able to recruit professionals, product managers, doctors, or educated participants.
3. Acknowledging Participant Contribution
Compensating participants reflects respect for their time and insights, fostering goodwill and encouraging future collaboration. As highlighted by People for Research,
“The right incentive can definitely make or break your research and user recruitment, as it can increase participation in your study, help to reduce drop-out rates, facilitate access to hard-to-reach groups, and ensure participants feel appropriately rewarded for their efforts.”
Types of Incentives: Monetary and Non-Monetary

Incentives can be broadly categorized into monetary and non-monetary rewards, each with its own set of advantages and considerations:
Monetary Incentives
These include direct financial compensation such as cash payments, gift cards, or vouchers. Monetary incentives are straightforward and often highly effective in motivating participation. However, the amount should be commensurate with the time and effort required, and mindful of not introducing undue influence or coercion.
As noted in a study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, “Research indicates that incentives improve response rates and that monetary incentives are more effective than non-monetary incentives.”
Non-Monetary Incentives
Non-monetary rewards include things like free products (e.g. keep the TV after testing), access to exclusive content, or charitable donations made on behalf of the participant.
The key here is that the incentive should be tangible and offer real value. In general, this means no contests, discounts to buy a product (that’s sales & marketing, not testing & research), swag, or “early access” as the primary incentive if your recruiting participants for the purpose of testing and user research. Those things can be part of the incentive, and they can be very useful as marketing tools for viral beta product launches, but they are not usually sufficient as a primary incentive.
However, this rule doesn’t apply in certain situations:
Well known companies / brands, and testing with your own users
If you have a well-known and desired brand or product with an avid existing base of followers, non monetary incentives can sometimes work great. Offering early access to new features or exclusive content can be a compelling incentive. If Tesla is offering free access to a new product, it’s valuable! But for most startups conducting user research, early access to your product is not usually as valuable as you think it is.
At BetaTesting, we work with many companies, big and small. We allow companies to recruit testers from our own panel of 450,000+ participants, or to recruit from their own users/customers/employees. Sometimes when our customers recruit from their own users and don’t offer an incentive, they get low quality participation. We have seen other times, for example, when we worked with the New York Times, that their existing customers were very passionate and eager to give feedback without any incentive being offered.
Impact of Incentives on Data Quality
While incentives are instrumental in boosting participation, they can also influence the quality of data collected:
- Positive Effects: Appropriate incentives can lead to increased engagement and more thoughtful responses, as participants feel their contributions are valued.
- Potential Challenges: Overly generous incentives may attract individuals primarily motivated by compensation, potentially leading to less genuine responses. Additionally, certain types of incentives might introduce bias; for example, offering product discounts could disproportionately attract existing customers, skewing the sample.
Great Question emphasizes the need for careful consideration:
“Using incentives in UX research can positively influence participant recruitment and response rates. The type of incentive offered—be it monetary, non-monetary, or account credits—appeals to different participant demographics, which may result in various biases.
Aligning Incentives with Research Objectives

A one-size-fits-all approach to incentives rarely works. To truly drive meaningful participation and valuable feedback, your incentives need to align with your research goals. Whether you’re conducting a usability study, bug hunt, or exploratory feedback session, the structure and delivery of your rewards can directly impact the quality and authenticity of the insights you collect.
Task-Specific Incentives
When you’re testing for specific outcomes—like bug discovery, UX issues, or task completions—consider tying your incentives directly to those outputs. This creates clear expectations and motivates participants to dig deeper. Some examples:
- If your goal is to uncover bugs in a new app version, offering a bonus based on the issues reported can encourage testers to explore edge cases and be more thorough. This approach also fosters a sense of fairness, as participants see a direct connection between their effort and their reward. For tests like QA/bug testing, a high quality test result might not include any bugs or failed test cases (that tester may not have encountered any issues!) so, be sure the base reward itself is fair, but that the bonus encourages quality bug reporting.
- If you need each tester to submit 5 photos, the incentive should be directly tied to the submission
- In a multi-day longitudinal test or journal study, you may design tasks and surveys specifically around feedback on features X, Y, Z, etc. It might be important to you to require that testers complete the full test to earn the reward. However, in this case of course the user behavior will not mirror what you can expect to see from your real users. If your goal of the test is to measure how your testers are engaging with your app (e.g. do they return on day 2, day 3, etc), then you definitely don’t want to tie your incentive to a daily participation requirement. Instead, you should encourage organic participation.
Incentives to Encourage Organic / Natural Behavior
If you’re trying to observe natural behavior—say, how users engage with your product over time or how they organically complete tasks—it’s better not to tie incentives to specific actions. Instead, offer a flat participation fee. This prevents you from inadvertently shaping behavior and helps preserve the authenticity of your findings.
This strategy works well in longitudinal studies, journal-based research, or when you want unbiased data around product adoption. It reduces pressure on the participant and allows for more honest feedback about friction points and usability concerns.
This SurveyMonkey article emphasizes the importance of being thoughtful about the type of incentive depending on the study:
“Non-monetary incentives are typically thank you gifts like a free pen or notebook, but can also be things like a brochure or even a charity donation.”
This reinforces that even simple gestures can be effective—especially when they feel genuine and aligned with the study’s tone and goals.
Clarity Is Key
Whatever structure you choose, be clear with your participants. Explain how incentives will be earned, what’s expected, and when they’ll receive their reward. Uncertainty around incentives is one of the fastest ways to lose trust—and respondents.
Aligning your incentive model with your research objectives doesn’t just improve the quality of your data—it shows your participants that you value their time, effort, and insights in a way that’s fair and aligned with your goals.
Matching Incentives to Participant Demographics
Offering incentives is not just about picking a number—it’s about understanding who you’re recruiting and what motivates them. Tailoring your incentives to match participant demographics ensures your offer is compelling enough to attract qualified testers without wasting budget on ineffective rewards.
Professionals and Specialists – When your research involves targeting professionals with unique industry knowledge (e.g.software engineers, doctors, teachers) giving the same incentives that might be offered to general consumers often will not work. In general, the more money that a person makes and the busier they are, the higher the incentive need to be to motivate them to take time out of their day to provide you with helpful feedback.
For these audiences, consider offering higher-value gift cards that correspond with the time required.
A quick aside: Many popular research platforms spread the word about how they offer “fair” incentives to testers. For example, a minimum of $8 per hour. It’s very common for clients to run 5 minute tests on these platforms where the testers get .41 (yes, 41 cents). And these research companies actually brag about that being fair! As a researcher, do you really think you’re targeting professionals, or people that make 100K+, to take a 5 minute test for 41 cents? Does the research platform offer transparency so you can know who the users are? If not, please use some common sense. You have your targeting criteria set to “100K+ developers”, but you’re really targeting desperate people that said they were developers that made 100K+.
General Consumers -For mass-market or B2C products, modest incentives like Amazon or Visa gift cards tend to work well—particularly when the tasks are short and low-effort. In these cases, your reward doesn’t need to be extravagant, but it does need to be meaningful and timely.
It’s also worth noting that digital incentives tend to perform better with younger, tech-savvy demographics.
“Interest in digital incentives is particularly prevalent among younger generations, more digitally-minded people and those who work remotely. As the buying power of Gen Z and millennials grows, as digitally savvy and younger people comprise a larger percentage of the workforce and as employees become more spread apart geographically, it will become increasingly vital for businesses to understand how to effectively motivate and satisfy these audiences.” – Blackhawk Network Research on Digital Incentives.
Mitigating Fraud and Ensuring Data Integrity

While incentives are a powerful motivator in user research, they can also open the door to fraudulent behavior if not managed carefully. Participants may attempt to game the system for rewards, which can skew results and waste time. That’s why implementing systems to protect the quality and integrity of your data is essential. Read our article about how AI impacts fraud in user research.
Screening Procedures
Thorough screening is one of the first lines of defense against fraudulent or misaligned participants.
Effective screeners include multiple-choice and open-ended questions that help assess user eligibility, intent, and relevance to your research goals. Including red herring questions (with obvious correct/incorrect answers) can also help flag inattentive or dishonest testers early.
If you’re targeting professionals or high income individuals, ideally you can actually validate that each participant is who they say they are and that they are a fit for your study. Platforms like BetaTesting allow you to see participant LinkedIn profiles during manual recruiting to provide full transparency.
Monitoring and Verification
Ongoing monitoring is essential for catching fraudulent behavior before or during testing. This includes tracking inconsistencies in responses, duplicate accounts, suspicious IP addresses, or unusually fast task completion times that suggest users are rushing through just to claim an incentive.
At BetaTesting, our tools include IP address validation, ID verification, SMS verification, behavior tracking, and other anti-fraud processes.
Virtual Incentives
Platforms that automate virtual rewards—like gift cards—should still include validation workflows. Tools like Tremendous often include built-in fraud checks or give researchers control to manually approve each reward before disbursement. Also, identity verification for higher-stakes tests is becoming more common.
When managed well, incentives don’t just drive engagement—they reward honest, high-quality participation. But to make the most of them, it’s important to treat fraud prevention as a core part of your research strategy.
Best Practices for Implementing Incentives
To maximize the effectiveness of incentives in user research, consider the following best practices:
- Align Incentives with Participants Expectations: Tailor the type and amount of incentive to match the expectations and preferences of your target demographic.
- Ensure Ethical Compliance: Be mindful of ethical considerations and institutional guidelines when offering incentives, ensuring they do not unduly influence participation.
- Communicate Clearly: Provide transparent information about the nature of the incentive, any conditions attached, and the process for receiving it.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Regularly assess the impact of incentives on participation rates and data quality, adjusting your approach as necessary to optimize outcomes.
By thoughtfully integrating incentives into your user research strategy, you can enhance participant engagement, reduce bias, and acknowledge the valuable contributions of your participants, ultimately leading to more insightful and reliable research outcomes.
Ultimately, the best incentive is one that feels fair, timely, and relevant to the person receiving it. By aligning your reward strategy with participant expectations, you’re not just increasing your chances of participation—you’re showing respect for their time and effort, which builds long-term goodwill and trust in your research process.
Incentives Aren’t Just a Perk—They’re a Signal

Incentives do more than encourage participation—they communicate that you value your testers’ time, input, and lived experience. In a world where people are constantly asked for their feedback, offering a thoughtful reward sets your research apart and lays the foundation for a stronger connection with your users.
Whether you’re running a short usability study or a multi-week beta test, the incentive structure you choose helps shape the outcome. The right reward increases engagement, drives higher-quality insights, and builds long-term trust. But just as important is how well those incentives align—with your goals, your audience, and your product experience.
Because when people feel seen, respected, and fairly compensated, they show up fully—and that’s when the real learning happens.
Now more than ever, as research becomes more distributed, automated, and AI-driven, this human touch matters. It reminds your users they’re not just test subjects in a system. They’re partners in the product you’re building.
And that starts with a simple promise: “Your time matters. We appreciate it.”
Have questions? Book a call in our call calendar.
-
Beta Testing MVPs to Find Product-Market Fit

Launching a new product is one thing; ensuring it resonates with users is another. In the pursuit of product-market fit (PMF), beta testing becomes an indispensable tool. It allows you to validate assumptions, uncover usability issues, and refine your core value proposition. When you’re working with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), early testing doesn’t just help you ship faster—it helps you build smarter.
Here’s what you’ll learn in this article:
- Refine Your Target Audience, Test With Different Segments
- When Is Your Product Ready for Beta Testing?
- What Types of Beta Tests Can You Run?
- Avoid Common Pitfalls
- From Insights to Iteration
- Build With Users, Not Just For Them
Refine Your Target Audience, Test With Different Segments
One of the biggest challenges in early-stage product development is figuring out exactly who you’re building for. Beta testing your MVP with a variety of user segments can help narrow your focus and guide product decisions. Begin by defining your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) and breaking it down into more general testable target audience groups groups based on demographics, interests, employment info, product usage, or whatever criteria is most important for you.
For example, Superhuman, the email client for power users, initially tested across a broad user base. But through iterative beta testing, they identified their most enthusiastic adopters: tech-savvy professionals who valued speed, keyboard shortcuts, and design. Read how they built Superhuman here.
By comparing test results across different segments, you can prioritize who to build for, refine messaging, and focus development resources where they matter most.
When Is Your Product Ready for Beta Testing?

The short answer: probably yesterday.
You don’t need a fully polished product. You don’t need a flawless UX. You don’t even need all your features live. What you do need is a Minimum Valuable Product—not just a “Minimum Viable Product.”
Let’s unpack that.
A Minimum Viable Product is about function. It asks: Can it run? Can users get from A to B without the app crashing? It’s the version of your product that technically works. But just because it works doesn’t mean it works well—or that anyone actually wants it.
A Minimum Valuable Product, on the other hand, is about learning. It asks: Does this solve a real problem? Is it valuable enough that someone will use it, complain about it, and tell us how to make it better? That’s the sweet spot for beta testing. You’re not looking for perfection—you’re looking for traction.
The goal of your beta test isn’t to impress users. It’s to learn from them. So instead of waiting until every feature is built and pixel-perfect, launch with a lean, focused version that solves one core problem really well. Let users stumble. Let them complain. Let them show you what matters.
Just make sure your MVP doesn’t have any show-stopping bugs that prevent users from completing the main flow. Beyond that? Launch early, launch often, and let real feedback shape the product you’re building.
Because the difference between “viable” and “valuable” might be the difference between a launch… and a lasting business.
What Types of Beta Tests Can You Run?
Beta testing offers a versatile toolkit to evaluate and refine your product. Depending on your objectives, various test types can be employed to gather specific insights. Here’s an expanded overview of these test types, incorporating real-world applications and referencing BetaTesting’s resources for deeper understanding:
Bug Testing
Also known as a Bug Hunt, this test focuses on identifying technical issues within your product. Testers explore the application, reporting any bugs they encounter, complete with device information, screenshots, and videos. This method is invaluable for uncovering issues across different devices, operating systems, and browsers that might be missed during in-house testing.
Usability Testing
In this approach, testers provide feedback on the user experience by recording their screens or providing selfie videos while interacting with your product. They narrate their thoughts, highlighting usability issues, design inconsistencies, or areas of confusion. This qualitative data helps in understanding the user’s perspective and improving the overall user interface.
Survey-Based Feedback
This method involves testers using your product and then completing a survey to provide structured feedback. Surveys can include a mix of qualitative and quantitative questions, offering insights into user satisfaction, feature preferences, and areas needing improvement. BetaTesting’s platform allows you to design custom surveys tailored to your specific goals.
Multi-Day Tests
These tests span several days, enabling you to observe user behavior over time. Testers engage with your product in their natural environment, providing feedback at designated intervals. This approach is particularly useful for assessing long-term usability, feature adoption, and identifying issues that may not surface in single-session tests.
User Interviews
Moderated User Interviews involve direct interaction with testers through scheduled video calls. This format allows for in-depth exploration of user experiences, motivations, and pain points. It’s especially beneficial for gathering detailed qualitative insights that surveys or automated tests might not capture. BetaTesting facilitates the scheduling and conducting of these interviews.
By strategically selecting and implementing these beta testing methods, you can gather comprehensive feedback to refine your product, enhance user satisfaction, and move closer to achieving product-market fit.
You can learn about BetaTesting test types here in this article, Different Test Types Overview
Avoid Common Pitfalls

Beta testing is one of the most powerful tools in your product development toolkit—but only when it’s used correctly. Done poorly, it can lead to false confidence, missed opportunities, and costly delays. To make the most of your beta efforts, it’s critical to avoid a few all-too-common traps.
Overbuilding Before Feedback
One of the most frequent mistakes startups make is overengineering their MVP before ever putting it in front of users. This often leads to wasted time and effort refining features that may not resonate with the market. Instead of chasing perfection, teams should focus on launching a “Minimum Valuable Product”—a version that’s good enough to test the core value with real users.
This distinction between “valuable” and “viable” is critical. A feature-packed MVP might seem impressive internally, but if it doesn’t quickly demonstrate its core utility to users, it can still miss the mark. Early launches give founders the opportunity to validate assumptions and kill bad ideas fast—before they become expensive distractions.
Take Superhuman, for example. Rather than racing to build everything at once, they built an experience tailored to a core group of early adopters, using targeted feedback loops to improve the product one iteration at a time. Their process became a model for measuring product-market fit intentionally, rather than stumbling upon it.
Ignoring Early Negative Signals
Beta testers offer something few other channels can: honest, early reactions to your product. If testers are disengaged, confused, or drop off early, those aren’t random anomalies—they’re warning signs.
Slack is a textbook case of embracing these signals. Originally built as a communication tool for the team behind a failed online game, Slack only became what it is today because its creators noticed how much internal users loved the messaging feature. Rather than cling to the original vision, they leaned into what users were gravitating toward.
“Understanding user behavior was the catalyst for Slack’s pivot,” as noted in this Medium article.
Negative feedback or disinterest during beta testing might be uncomfortable, but it’s far more useful than polite silence. Listen closely, adapt quickly, and you’ll dramatically increase your chances of building something people actually want.
Recruiting the Wrong Testers
You can run the best-designed test in the world, but if you’re testing with the wrong people, your results will be misleading. Beta testers need to match your target audience. If you’re building a productivity app for remote knowledge workers, testing with high school students won’t tell you much.
It’s tempting to cast a wide net to get more feedback—but volume without relevance is noise. Targeting the right audience helps validate whether you’re solving a meaningful problem for your intended users.
To avoid this, get specific. Use targeted demographics, behavioral filters, and screening questions to ensure you’re talking to the people your product is actually meant for. If your target audience is busy parents or financial analysts, design your test and your outreach accordingly.
Failing to Act on Findings
Finally, the most dangerous mistake of all is gathering great feedback—and doing nothing with it. Insight without action is just noise. Teams need clear processes for reviewing, prioritizing, and implementing changes based on what they learn.
That means not just reading survey responses but building structured workflows to process them.
Tools like Dovetail, Notion, or even Airtable can help turn raw feedback into patterns and priorities.
When you show testers that their feedback results in actual changes, you don’t just improve your product—you build trust. That trust, in turn, helps cultivate a loyal base of early adopters who stick with you as your product grows.
From Insights to Iteration
Beta testing isn’t just a checkbox you tick off before launch—it’s the engine behind product improvement. The most successful teams don’t just collect feedback; they build processes to act on it. That’s where the real value lies.
Think of beta testing as a continuous loop, not a linear process. Here’s how it works:
Test: Launch your MVP or new feature to real users. Collect their experiences, pain points, and observations.
Learn: Analyze the feedback. What’s confusing? What’s broken? What do users love or ignore? Use tools like Dovetail for tagging and categorizing qualitative insights, or Airtable/Notion to organize feedback around specific product areas.
Iterate: Prioritize your learnings. Fix what’s broken. Improve what’s clunky. Build what’s missing. Share updates internally so the whole team aligns around user needs.
Retest: Bring those changes back to users. Did the fix work? Is the feature now useful, usable, and desirable? If yes—great. If not—back to learning.
Each round makes your product stronger, more user-centered, and closer to product-market fit. Importantly, this loop is never really “done.” Even post-launch, you’ll use it to guide ongoing improvements, reduce churn, and drive adoption.
Superhuman – the premium email app, famously built a system to measure product-market fit using Sean Ellis’ question: “How disappointed would you be if Superhuman no longer existed?” They only moved forward after more than 40% of users said they’d be “very disappointed.” But they didn’t stop there—they used qualitative feedback from users who weren’t in that bucket to understand what was missing, prioritized the right features, and iterated rapidly.The lesson? Beta testing is only as powerful as what you do after it. Check the full article here.
Build With Users, Not Just For Them
Product-market fit isn’t discovered in isolation. Finding product-market fit isn’t a milestone you stumble into—it’s something you build, hand-in-hand with your users. Every bug report, usability hiccup, or suggestion is a piece of the puzzle, pointing you toward what matters most. Beta testing isn’t just about polishing what’s already there—it’s about shaping what’s next.
When you treat your early users like collaborators instead of just testers, something powerful happens: they help you uncover the real magic of your product. That’s how Superhuman refined its feature set – by listening, learning, and looping.
The faster you start testing, the sooner you’ll find what works. And the deeper you engage with real users, the more confident you’ll be that you’re building something people want.
So don’t wait for perfect. Ship what’s valuable, listen closely, and iterate with purpose. The best MVPs aren’t just viable – they’re valuable. And the best companies? They build alongside their users every step of the way.
Have questions? Book a call in our call calendar.
-
AI-Powered User Research: Fraud, Quality & Ethical Questions

This article is part of a series of articles focused on AI in user research. To get started, read about the State of AI in User Research and Testing in 2025.
AI is transforming how companies conduct user research and software testing. From automating tedious analysis to surfacing insights at lightning speed, the benefits are real—and they’re reshaping how teams build, test, and launch products. But with that transformation comes a new layer of complexity.
We’re entering an era where AI can write surveys, analyze video feedback, detect bugs, and even simulate participants. It’s exciting—but also raises serious questions: What happens when the testers aren’t real? Can you trust feedback that’s been filtered—or even generated—by AI? And what ethical guardrails should be in place to ensure fairness, transparency, and integrity?
As AI grows more human-like in how it speaks, behaves, and appears, the line between authentic users and synthetic actors becomes increasingly blurred. And when the research driving your product decisions is based on uncertain sources, the risk of flawed insights grows dramatically.
Here’s what you’ll learn in this article:
- Trust and Identity Verification in an AI-Driven World
- Loss of Creativity & Depth in Research
- Bias in AI-Driven Research & Testing
- Transparency & Trust in AI-Driven Research
- Job Displacement: Balancing Automation with Human Expertise
- The Risk of Fake User Counts & Testimonials
- The Ethics of AI in Research: Where Do We Go From Here?
Trust and Identity Verification in an AI-Driven World

Note: This person does not exist! As AI gets smarter and more human-like, one of the biggest questions we’ll face in user research is: Can we trust that what we’re seeing, hearing, or interacting with is actually coming from a real person? With AI now capable of generating human-like voices, hyper-realistic faces, and entire conversations, it’s becoming harder to distinguish between authentic human participants and AI-generated bots.
This isn’t hypothetical—it’s already happening. Tools like ChatGPT and Claude can hold detailed conversations, while platforms like ElevenLabs can clone voices with startling accuracy, and This Person Does Not Exist generates realistic profile photos of people who don’t exist at all (ThisPersonDoesNotExist). As impressive as these technologies are, they also blur the line between real and synthetic behavior, and that poses a significant risk for research and product testing.
“Amazon is filled with fake reviews and it’s getting harder to spot them”, from CNBC. And that was from 2020, before the rise of AI.
Across the web, in platforms like Amazon, YouTube, LinkedIn and Reddit, there’s growing concern over bots and fake identities that engage in discussions, test products, and even influence sentiment in ways that appear completely human.
In research settings, this could mean collecting feedback from non-existent users, making flawed decisions, and ultimately losing trust in the insights driving product strategy.
That’s why identity verification is quickly becoming a cornerstone of trust in user research. Tools like Onfido and Jumio are leading the charge by helping companies verify participants using government-issued IDs, biometrics, and real-time facial recognition (Onfido, Jumio). These technologies are already standard in high-stakes industries like fintech and healthcare—but as AI-generated personas become more convincing, we’ll likely see these safeguards expand across every area of digital interaction.
For companies conducting user research and testing, it’s critical to have confidence that you’re testing with the right audience. At BetaTesting, we’ve implemented robust anti-fraud and identity controls, including identity verification, IP validation, SMS validation, no VPNs allowed for testers, behavioral analysis, and more. We’ve seen fraud attempts increasing first hand over the years, and we have built tools ensure we address the issue head-on and continue to focus on participant quality.
Looking ahead, identity verification won’t just be a nice-to-have—it’ll be table stakes. Whether you’re running a beta test, collecting user feedback, or building an online community, you’ll need ways to confidently confirm that the people you’re hearing from are, in fact, people.
In a world where AI can walk, talk, type, and even smile like us, the ability to say “this is a real human” will be one of the most valuable signals we have. And the platforms that invest in that trust layer today will be the ones that thrive tomorrow.
Loss of Creativity & Depth in Research

While AI excels at identifying patterns in data, it struggles with original thought, creative problem-solving, and understanding the nuance of human experiences. This is a key limitation in fields like user research, where success often depends on interpreting emotional context, understanding humor, recognizing cultural cues, and exploring new ideas—areas where human intuition is essential.
Text based AI-analysis tools can efficiently categorize and summarize feedback, but they fall short in detecting sarcasm, irony, or the subtle emotional undertones that often carry significant meaning in user responses. These tools rely on trained language models that lack lived experience, making their interpretations inherently shallow.
“Is empathy the missing link in AI’s cognitive function? Thinking with your head, without your heart, may be an empty proposition.” (Psychology Today)
Organizations that lean too heavily on AI risk producing surface-level insights that miss the richness of real user behavior, which can lead to flawed decisions and missed opportunities for innovation. True understanding still requires human involvement—people who can read between the lines, ask the right follow-up questions, and interpret feedback with emotional intelligence.
Bias in AI-Driven Research & Testing
AI models are only as objective as the data they’re trained on. When datasets reflect demographic, cultural, or systemic biases, those biases are not only preserved in the AI’s output—they’re often amplified. This is especially problematic in user research and software testing, where decisions based on flawed AI interpretations can affect real product outcomes and user experiences.
Amazon famously scrapped its AI recruiting tool that showed bias against Women.
“If an algorithm’s data collection lacks quantity and quality, it will fail to represent reality objectively, leading to inevitable bias in algorithmic decisions.“ This research article from Nature reports on how discrimination in artificial intelligence-enabled recruitment practices exist because their training data is often drawn from past hiring practices that carried historical bias.
Similarly, Harvard Business Review highlighted how AI sentiment analysis tools can misinterpret responses due to an inability to understand nuances with language, tone, and idioms. This leads to inaccurate sentiment classification, which can distort research insights and reinforce cultural bias in product development (Harvard Business Review).
To reduce bias, companies must regularly audit AI systems for fairness, ensure that models are trained on diverse, representative data, and maintain human oversight to catch misinterpretations and anomalies. Without these checks in place, AI-powered research may reinforce harmful assumptions instead of surfacing objective insights.
Transparency & Trust in AI-Driven Research
As AI becomes more deeply integrated into research, transparency is no longer optional—it’s essential. Participants and stakeholders alike should understand how AI is used, who is behind the analysis, and whether human review is involved. Transparency builds trust, and without it, even the most advanced AI tools can sow doubt.
Among those who’ve heard about AI, 70% have little to no trust in companies to make responsible decisions about how they use it in their products. (Pew Research).
To maintain transparency, companies should clearly state when and how AI is used in their research and user testing processes. This includes disclosing the extent of human involvement, being upfront about data sources, and ensuring participants consent to AI interaction. Ethical use of AI starts with informed users and clear communication.
Job Displacement: Balancing Automation with Human Expertise
One of the most prominent concerns about AI in research and software testing is its potential to displace human professionals. AI has proven to be highly effective in automating repetitive tasks, such as analyzing large datasets, summarizing survey results, detecting bugs, and generating basic insights. While this efficiency brings clear productivity gains, it also raises concerns about the long-term role of human researchers, analysts, and QA testers.
A 2023 report from the World Economic Forum projected that AI and technology automation will be the biggest factor in displacing up to 83 million jobs globally by 2025 – Read full report here
However, the same report highlighted a more optimistic side: an estimated 69 million new jobs could emerge, with popular growing roles including: Data Analysts/Scientists, AI and Machine Learning Specialists, and Digital Transformation Specialists
This duality underlines an important truth: AI should be seen as a collaborative tool, not a replacement. Companies that effectively balance automation with human expertise can benefit from increased efficiency while preserving critical thinking and innovation. The most successful approach is to use AI for what it does best—speed, scale, and consistency—while entrusting humans with tasks that demand creativity, ethical reasoning, and user empathy.
The Risk of Fake User Counts & Testimonials

AI can generate highly realistic synthetic content, and while this technology has productive uses, it also opens the door to manipulated engagement metrics and fake feedback. In research and marketing, this presents a significant ethical concern.
A 2023 report by the ACCC found that approximately one in three online reviews may be fake, often generated by bots or AI tools. These fake reviews mislead consumers and distort public perception, and when used in research, they can invalidate findings or skew user sentiment. The FTC also recently banned fake review/testimonials.
In product testing, synthetic users can create false positives, making products appear more successful or more user-friendly than they really are. If left unchecked, this undermines the authenticity of feedback, leading to poor product decisions and damaged customer trust.
To maintain research integrity, companies should distinguish clearly between real and synthetic data, and always disclose when AI-generated insights are used. They should also implement controls to prevent AI from producing or spreading fake reviews, testimonials, or inflated usage data.
The Ethics of AI in Research: Where Do We Go From Here?
As AI becomes a staple in research workflows, companies must adopt ethical frameworks that emphasize collaboration between human expertise and machine intelligence. Here’s how they can do it responsibly:
Responsible AI Adoption means using AI to augment—not replace—human judgment. AI is powerful for automation and analysis, but it lacks the intuition, empathy, and real-world perspective that researchers bring. It should be used as a decision-support tool, not as the final decision-maker.
AI as a Research Assistant, Not a Replacement is a more realistic and productive view. AI can take on repetitive, time-consuming tasks like data aggregation, pattern detection, or automated transcription, freeing up humans to handle interpretation, creative problem-solving, and ethical oversight.
Ethical Data Use & Transparency are critical to building trust. Companies must ensure fairness in AI-driven outputs, openly communicate how AI is used, and take full accountability for its conclusions. Transparency also involves participant consent and ensuring data collection is secure and respectful.
AI & Human Collaboration should be the guiding principle. When researchers and machines work together, they can unlock deeper insights faster and at scale. The key is ensuring AI tools are used to enhance creativity, not limit it—and that human voices remain central to the research process.
Final Thoughts
AI is reshaping the future of user research and software testing—and fast. But for all the speed, automation, and scalability it brings, it also introduces some very human questions: Can we trust the data? Are we losing something when we remove the human element? What’s the line between innovation and ethical responsibility?
The truth is, AI isn’t the villain—and it’s not a silver bullet either. It’s a tool. A powerful one. And like any tool, the value it delivers depends on how we use it. Companies that get this right won’t just use AI to cut corners—they’ll use it to level up their research, spot issues earlier, and make better decisions, all while keeping real people at the center of the process.
So, whether you’re just starting to experiment with AI-powered tools or already deep into automation, now’s the time to take a thoughtful look at how you’re integrating AI into your workflows. Build with transparency. Think critically about your data. And remember: AI should work with your team—not replace it.
Ethical, human-centered AI isn’t just the right move. It’s the smart one.
Have questions? Book a call in our call calendar.
-
When to Launch Your Beta Test

Timing is one of the most important things to consider when it comes to launching a successful beta test, but maybe not in the way that you think. The moment you introduce your product to users can greatly impact participation, engagement, and your ability to learn from users through the feedback you receive. So, how do you determine the perfect timing? Let’s break it down.
Start Early Rather Than Waiting for the Perfect Moment

The best time to start testing is as soon as you have a functional product. If you wait until everything is fully polished, you risk missing out on valuable feedback that could shape development. Before you launch, there’s one crucial decision to make: What’s your primary goal? Is your beta test focused on improving your product, or is it more about marketing? If your goal is product development, iterative testing will help you refine features, usability, and functionality based on real user feedback.
Beta testing is primarily about making improvements—not just generating hype. However, if your goal is to create buzz, a larger beta test before launch can attract attention and build anticipation. This marketing-driven approach is different from testing designed to refine your product (see Using Your Beta Launch to Go Viral, below).
Make Sure Your Product’s Core Functionality Works
Your product doesn’t need to be perfect, but it should be stable and functional enough for testers to engage with it meaningfully. Major bugs and usability issues should be addressed, and the product should offer enough functionality to gather valuable feedback. The user experience must also be intuitive enough to reduce onboarding friction. Running through the entire test process yourself before launching helps identify any major blockers that could limit the value of feedback. Additionally, make sure testers can access the product easily and get started without unnecessary delays.
At BetaTesting, we emphasize iterative testing rather than waiting for a “seamless user experience.” Our platform is designed to help you gather feedback continuously and improve your product over time.
Iterate, Iterate, Iterate…

Testing shouldn’t be a one-time event—it should be an ongoing process that evolves with your product. Running multiple test cycles ensures that improvements align with user expectations and that changes are validated along the way. At BetaTesting, we help companies test throughout the entire product development process, from early research to live product improvements. Since we focus on the beta testing phase, we specialize in testing products that are already functional rather than just mockups. Testing is valuable not just before launch but also on an ongoing basis to support user research or validate new features.
Have The Team Ready

A successful beta test requires a dedicated team to manage, analyze, and act on feedback. You should have a team ready to assist testers, a feedback collection and analysis system should be in place, and developers should be on standby to address critical issues. Assigning a single point of contact to oversee the beta test is highly recommended. This person can coordinate with BetaTesting, manage schedules with the development team, and handle tester access.
We also encourage active engagement with testers, as this helps increase participation and ensures quick issue resolution. However, BetaTesting is designed to be easy to use, so if your team prefers to collect feedback and act on it later without real-time interaction, that’s completely fine too.
Align with Your Business Goals
Your beta test should fit seamlessly into your overall product roadmap. If you have an investor pitch or public launch coming up, give yourself enough time to collect and analyze feedback before making final decisions. Planning for adequate time to implement feedback before launch, considering fixed deadlines such as investor meetings or PR announcements, and avoiding last-minute rushes that could compromise testing effectiveness are all essential factors. For situations where quick insights are needed, BetaTesting offers an expedited testing option that delivers results within hours, helping you meet tight deadlines without sacrificing quality.
Using Your Beta Launch to Go Viral
For some companies, a beta launch is viewed more as a marketing event: an opportunity to generate hype and capitalize on FOMO and exclusivity in order to drive more signups and referrals. This can work amazingly well, but it’s important to separate marketing objectives from product-focused objectives. For most companies, your launch is not going to go viral. The road to a great product and successful business is often fraught with challenges and it can often take years to really find product-market fit.
Final Thoughts

Don’t wait to choose the perfect time to start testing. While you can use your beta launch as a marketing tool, we recommend instead focusing most of your effect on testing for the purpose of gathering feedback and improving your product. Think about your product readiness, internal resources, and strategic goals. Iterative testing helps you gather meaningful user feedback, build relationships with early adopters, and set the stage for a successful launch. Start early, stay user-focused, and keep improving—your product (and your users) will thank you!
Have questions? Book a call in our call calendar.
-
Global creative agency adam&eve leads with human-centered design
Award winning creative agency adam&eve (voted Ad Agency of the Year by AdAge) partners with BetaTesting to inspire product development with a human centered design process.
In today’s fast-paced market, developing products that resonate with users is more critical than ever. A staggering 70% of product launches fail due to a lack of user-centered design and insight. This statistic underscores a fundamental truth: understanding and prioritizing the needs and experiences of users is essential for success.
As adam&eve works with enterprise clients to create and market new digital experiences, they have often turned to BetaTesting to power real-world testing and user research.
Understanding Traveler Opinions & Use of Comparison Booking Tools

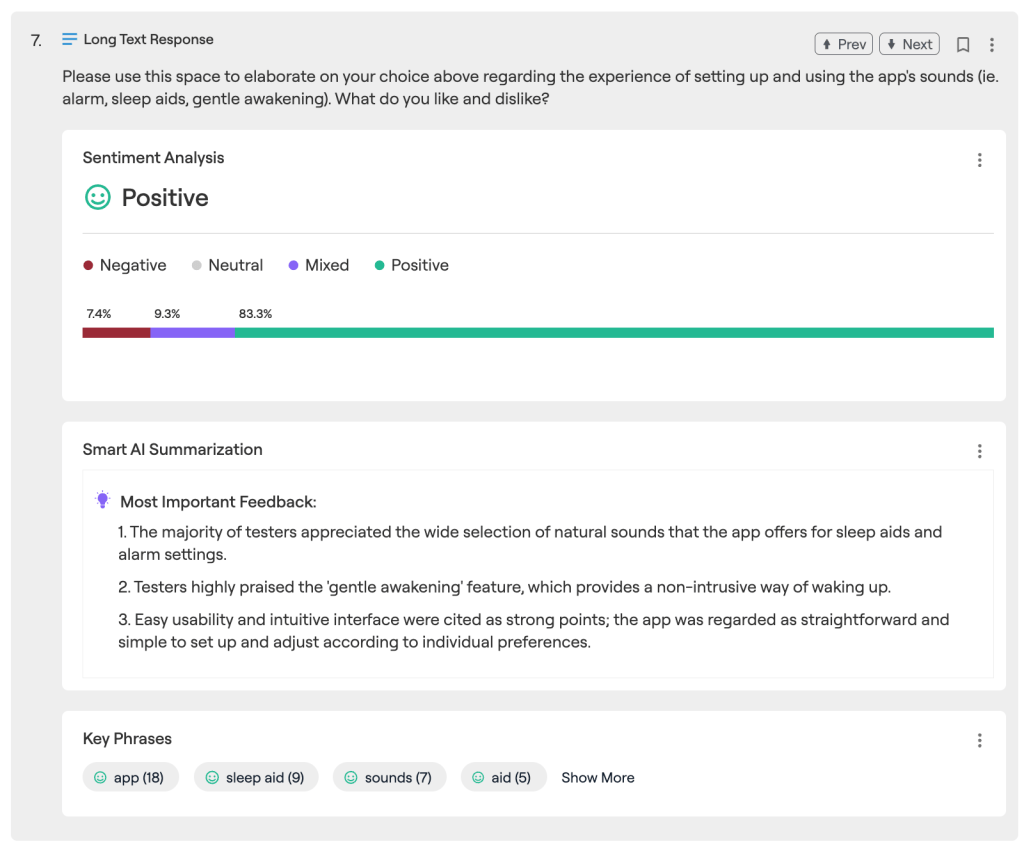
For a large US airline client, BetaTesting recruited and screened participants across a representative mix of demographic and lifestyle criteria. Participants completed in-depth surveys and recorded themselves answering various questions on selfie videos. Later users recorded their screen and spoke their thoughts out loud while using travel comparison tools to book travel. The BetaTesting platform processed and analyzed the videos with AI (along with transcripts, key phrases, sentiment, and summarization) and the professional services team provided an in-depth custom summary report with analysis and observations.
Sara Chapman, Executive Experience Strategy Director, adam&eve:
“Working with BetaTesting has allowed us to bring in a far more human centered design process and ensure we’re testing and evolving our products with real users across the whole of our development cycle. The insights we’ve gained from working with the BetaTesting community have been vital in shaping the features, UX and design of our product and has enabled us to take a research driven approach to where we take the product next.”
Beta Testing for an Innovative Dog Nose Scan Product

Every year, millions of pets go missing, creating distressing situations for families and pet owners alike. In fact, it’s estimated that 10 million pets are lost or stolen in the United States annually. Amid this crisis, innovative solutions are essential for reuniting lost pets with their families. Remarkably, recent advancements in pet identification have highlighted the uniqueness of dog nose prints. Just as human fingerprints are one-of-a-kind, each dog’s nose print is distinct due to its unique pattern of ridges and grooves.
Adam&eve worked with an enterprise client to develop a new app which leveraged the uniqueness of dog nose prints as a promising solution to the problem of lost pets.
BetaTesting helped organize numerous real world tests to collect real-world data and feedback from pet owners:
- Participants tested the nose scan functionality and provided feedback on the user experience scanning their dog’s nose
- The software was tested in various lighting conditions to improve the nose print detection technology
- Hundreds of pictures were collected to improve AI models to accurately identify each dog’s nose
Learn about how BetaTesting.com can help your company launch better products with our beta testing platform and huge community of global testers.